promise A+
promise A+
promise A+规范
Promise/A+规范一共有10条规范,具体如下:
- Promise 状态
Promise 有三种状态:pending(进行中)、fulfilled(已成功)和rejected(已失败)。
- then 方法
Promise 必须提供 then 方法,用于注册在 Promise 状态确定后的回调函数。
- then 方法的参数
then 方法必须接收两个函数作为参数,分别为 Promise 状态被 fulfilled 时的回调函数 onFulfilled 和 Promise 状态被 rejected 时的回调函数 onRejected。
- then 方法的返回值
then 方法必须返回一个新的 Promise 对象,用于链式调用。
- then 方法的调用时机
onFulfilled 和 onRejected 只有在 Promise 状态确定后才会被调用,且调用次数不超过一次。
- then 方法的调用顺序
then 方法可以被同一个 Promise 对象多次调用,并且必须按照其注册顺序依次执行。
- then 方法的异常处理
如果 onFulfilled 或 onRejected 抛出异常,则新的 Promise 对象必须被 rejected。
- then 方法的参数可选
then 方法的参数 onFulfilled 和 onRejected 是可选的。
- Promise 解决过程
Promise 解决过程是指 Promise 从初始状态开始,最终转换为 fulfilled 或 rejected 的过程。
- Promise 解决过程的处理
Promise 解决过程中需要进行一系列的处理,包括状态转换、回调函数的调用、异常处理等。其中,then 方法的返回值需要根据 Promise 的状态和回调函数的返回值进行判断。
Promise的完整源码
INFO
Promise/A+规范的实现
在以下代码中,我们使用了类的形式来实现Promise。在构造函数中,我们初始化了Promise的状态、值和原因,并且定义了一个存储回调函数的数组。然后,我们定义了两个函数resolve和reject,用于将Promise的状态从pending改变为fulfilled或rejected,并且执行相应的回调函数。
在then函数中,我们判断当前Promise的状态,如果是fulfilled或rejected,则执行相应的回调函数,并且将返回值传入到resolvePromise函数中进行处理。如果是pending状态,我们将回调函数存储到数组中,等待Promise状态改变后再执行。 在catch函数和finally函数中,我们都是调用then函数,只是传入的回调函数不同。
在Promise.all方法中,我们返回一个新的Promise,并且等待传入的所有Promise全部解决后才返回结果。我们使用result数组保存每个Promise的解决值,并且使用counter变量记录已经解决的Promise数量。如果所有Promise都解决了,我们将result数组传递给新的Promise进行解决。如果有任何一个Promise被拒绝,我们直接拒绝新的Promise。注意,我们使用Promise.resolve方法将传入的值转换为Promise,以便在处理时统一处理。
最后,我们定义了resolvePromise函数,用于处理回调函数的返回值,并且将它们传递给下一个Promise。如果返回值是一个Promise,则需要等待它的状态改变后再执行下一个Promise的回调函数。如果返回值是一个普通值,则直接传递给下一个Promise。如果返回值是一个循环引用,则抛出异常。
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = 'pending';
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === 'pending') {
this.status = 'fulfilled';
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === 'pending') {
this.status = 'rejected';
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : (value) => value;
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === 'function'
? onRejected
: (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === 'fulfilled') {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
}
if (this.status === 'rejected') {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
}
if (this.status === 'pending') {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
});
}
});
return promise2;
}
catch(onRejected) {
return this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(callback) {
return this.then(
(value) => Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value),
(reason) =>
Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => {
throw reason;
})
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve(value);
});
}
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(reason);
});
}
static all(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
let counter = 0;
promises.forEach((promise, index) => {
Promise.resolve(promise)
.then((value) => {
result[index] = value;
counter++;
if (counter === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
})
.catch((reason) => {
reject(reason);
});
});
});
}
}
function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) {
if (promise2 === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise'));
}
let called = false;
if (x != null && (typeof x === 'object' || typeof x === 'function')) {
try {
const then = x.then;
if (typeof then === 'function') {
then.call(
x,
(y) => {
if (called) {
return;
}
called = true;
resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
},
(r) => {
if (called) {
return;
}
called = true;
reject(r);
}
);
} else {
resolve(x);
}
} catch (e) {
if (called) {
return;
}
called = true;
reject(e);
}
} else {
resolve(x);
}
}
复习promise的使用
有三种状态,pending(进行中)、fulfilled(已成功)、rejected(已失败)
new promise(resolve,reject)会声明一个promise实例,执行resolve会走then方法中的第一个回调(成功),执行reject会执行then方法中的第二个回调(失败)。then方法中不论第一个回调还是第二个回调执行成功了会接着走下一个then中的第一个回调,如果报错了会走下一个then中的第二个回调。
// 非管控异步操作
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve 和 reject是自己任意执行的,但是一般情况下,大家够约定成功执行resolve,失败执行reject
// excutor函数(执行函数)中可以不管控异步操作(但是不管控异步没什么意义)
resolve(100);
}).then(result => {
// resolve执行的时候会触发第一个回调函数执行
console.log(1)
return 1000; // 会把这个值传递给下一个then中的方法,如果返回的是一个新的promise实例,则等到promise处理完成,把处理完成的结果传递给下一个then
}, reason => {
// reject执行的时候会触发第二个回调函数执行
console.log(2)
}).then(result => { // 需要保证then方法返回的依然是promise实例,这样才可以实现链式调用
// 上一个then中管控的两个方法只要任何一个执行不报错,都会执行这个then中的第一个方法,如果执行报错,会执行此then中的第二个回调函数
}).catch(reason=>{
// catch就相当于then(null,reason=>{})
})
console.log(3)
// 等待所有的promise都成功执行then,反之只要有一个失败就会执行catch
Promise.all([promise1,promise2,promise3,promise4]).then();
封装基础版的promise库
没有实现then链
/* promise.js */
class Promise {
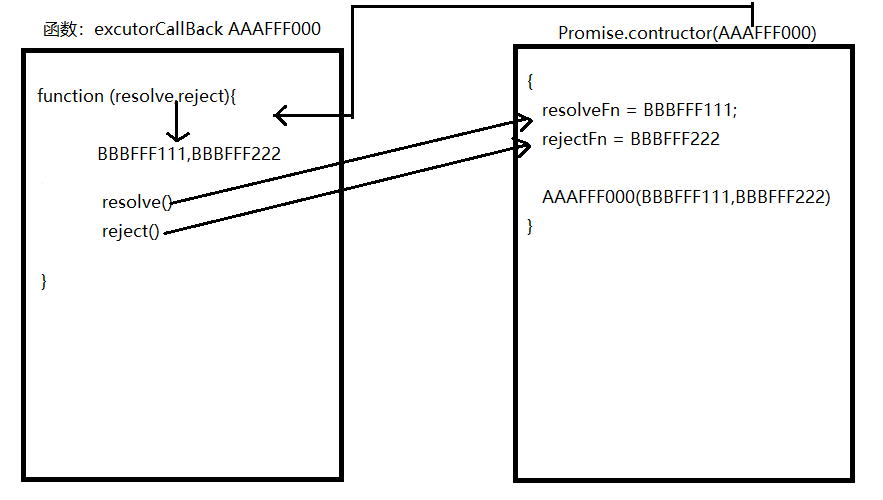
constructor(excutorCallback) {
this.status = 'pending'
this.value = undefined;
this.fulfilledAry = [];
this.rejectedAry = [];
// 执行excutor
let resolveFn = result => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'fulfilled';
this.value = result;
this.fulfilledAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
let rejectFn = reason => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'rejected';
this.value = reason;
this.rejectedAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
excutorCallback(resolveFn, rejectFn)
}
then (fulfilledCallBack, rejectedCallBack) {
this.fulfilledAry.push(fulfilledCallBack)
this.rejectedAry.push(rejectedCallBack)
}
}
// commonjs规范
module.exports = Promise;
/* test.js */
let Promise = require('./promise')
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve和reject只能执行一个,执行其中一个另一个就不会执行
setTimeout(() => {
Math.random() < 0.5 ? resolve(100) : reject(-100)
}, 1000);
}).then(result => {
console.log(result)
}, reason => {
console.log(reason)
});
console.log(3)
异常报错按照rejected状态处理
/* promise.js */
class Promise {
constructor(excutorCallback) {
this.status = 'pending'
this.value = undefined;
this.fulfilledAry = [];
this.rejectedAry = [];
// 执行excutor(异常捕获)
let resolveFn = result => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'fulfilled';
this.value = result;
this.fulfilledAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
let rejectFn = reason => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'rejected';
this.value = reason;
this.rejectedAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
try {
excutorCallback(resolveFn, rejectFn)
} catch (err) {
rejectFn(err);
}
}
then (fulfilledCallBack, rejectedCallBack) {
this.fulfilledAry.push(fulfilledCallBack)
this.rejectedAry.push(rejectedCallBack)
}
}
// commonjs规范
module.exports = Promise;
/* test.js */
let Promise = require('./promise')
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve和reject只能执行一个,执行其中一个另一个就不会执行
setTimeout(() => {
// 定时器中不能手动抛异常
Math.random() < 0.5 ? resolve(100) : reject(-100)
}, 1000);
throw new Error('ERROR');
}).then(result => {
console.log(result)
}, reason => {
console.log(reason)
});
console.log(3)
实现then方法的链式调用
// promise.js
class Promise {
constructor(excutorCallback) {
this.status = 'pending'
this.value = undefined;
this.fulfilledAry = [];
this.rejectedAry = [];
// 执行excutor(异常捕获)
let resolveFn = result => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'fulfilled';
this.value = result;
this.fulfilledAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
let rejectFn = reason => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'rejected';
this.value = reason;
this.rejectedAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
try {
excutorCallback(resolveFn, rejectFn); // 返回两个回调函数,每个回调函数都需要传参
} catch (err) {
rejectFn(err);
}
}
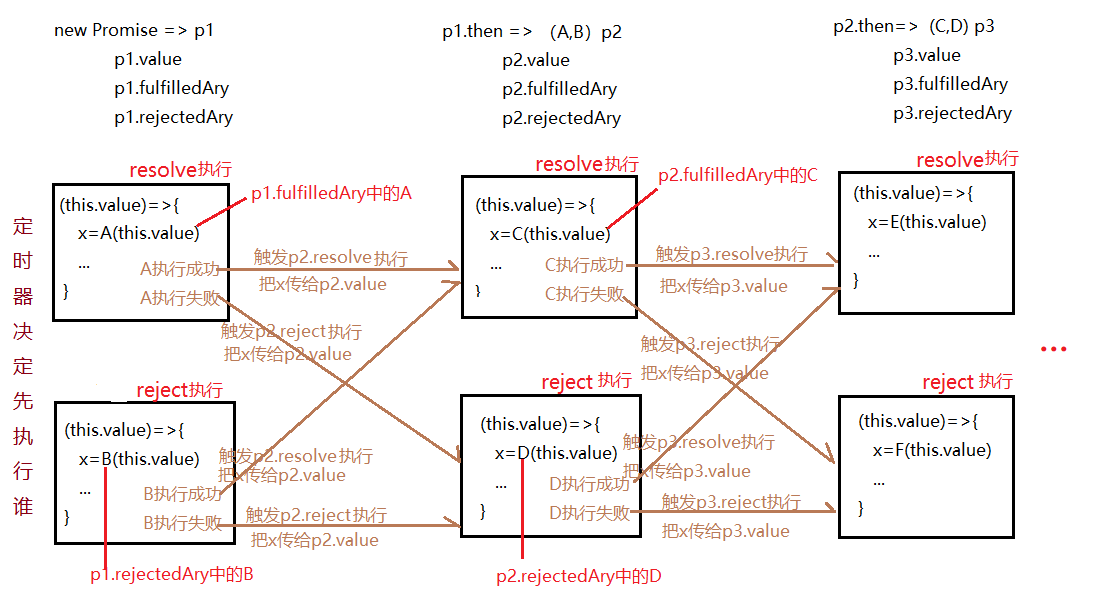
then (fulfilledCallBack, rejectedCallBack) {
// 返回一个新的promise实例
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// this从上文找是最初的promise实例,不是最新的
this.fulfilledAry.push(() => {
try {
let x = fulfilledCallBack(this.value);
// 返回的x有可能是普通值也有可能还是一个promise实例
x instanceof Promise ? x.then(resolve, reject) : resolve(x)
} catch (err) {
reject(err);
}
})
this.rejectedAry.push(() => {
try {
let x = rejectedCallBack(this.value);
x instanceof Promise ? x.then(resolve, reject) : resolve(x)
} catch (err) {
reject(err);
}
})
})
}
}
// commonjs规范
module.exports = Promise;
// test.js
let Promise = require('./promise')
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve和reject只能执行一个,执行其中一个另一个就不会执行
setTimeout(() => {
// 定时器中不能手动抛异常
Math.random() < 0.5 ? resolve(100) : reject(-100)
}, 1000);
// throw new Error('ERROR');
})
let p2 = p1.then(result => {
throw new Error('@')
return result + 100;
}, reason => {
return reason + 100;
});
let p3 = p2.then(result => {
console.log(p1 === p2); // false 执行then返回的是一个新的promise实例
console.log(result)
}, reason => {
console.log(reason)
})
console.log(3)
实现promise.all方法
class Promise {
constructor(excutorCallback) {
this.status = 'pending'
this.value = undefined;
this.fulfilledAry = [];
this.rejectedAry = [];
// 执行excutor(异常捕获)
let resolveFn = result => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'fulfilled';
this.value = result;
this.fulfilledAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
let rejectFn = reason => {
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
if (this.status !== 'pending') return;
this.status = 'rejected';
this.value = reason;
this.rejectedAry.forEach(item => item(this.value))
}, 0);
}
try {
excutorCallback(resolveFn, rejectFn); // 返回两个回调函数,每个回调函数都需要传参
} catch (err) {
rejectFn(err);
}
}
then (fulfilledCallBack, rejectedCallBack) {
typeof fulfilledCallBack !== 'function' ? fulfilledCallBack = result => result : null;
typeof rejectedCallBack !== 'function' ? rejectedCallBack = reason => { throw new Error(reason instanceof Error ? reason.message : reason) } : null;
// 返回一个新的promise实例
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// this从上文找是最初的promise实例,不是最新的
this.fulfilledAry.push(() => {
try {
let x = fulfilledCallBack(this.value);
// 返回的x有可能是普通值也有可能还是一个promise实例
x instanceof Promise ? x.then(resolve, reject) : resolve(x)
} catch (err) {
reject(err);
}
})
this.rejectedAry.push(() => {
try {
let x = rejectedCallBack(this.value);
x instanceof Promise ? x.then(resolve, reject) : resolve(x)
} catch (err) {
reject(err);
}
})
})
}
catch (rejectedCallBack) {
return this.then(null, rejectedCallBack)
}
// 私有属性
static all (promiseAry = []) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// index:记录成功的数量 result:记录成功的结果
let index = 0,
result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < promiseAry.length; i++) {
// promiseAry[i]:每一个需要处理的promise实例
promiseAry[i].then(val => {
index++;
result[i] = val; // 索引需要和promiseAry对应上,保证结果的顺序和数组顺序一致
if (index === promiseAry.length) {
resolve(result)
}
}, reject)
}
})
}
}
// commonjs规范
module.exports = Promise;
// test.js
let Promise = require('./6.promise')
/* let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve和reject只能执行一个,执行其中一个另一个就不会执行
setTimeout(() => {
// 定时器中不能手动抛异常
// Math.random() < 0.5 ? resolve(100) : reject(-100)
}, 1000);
resolve(100)
// throw new Error('ERROR');
})
let p2 = p1.then(result => {
return result + 100;
});
let p3 = p2.then(result => {
console.log(result)
throw new Error('222')
}).catch(reason => {
console.log(reason)
})
console.log(3) */
let p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(100)
}, 50);
})
let p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(200)
}, 10);
})
let p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(300)
}, 80);
})
Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]).then(result => {
// 所有的promise都成功执行,result中分别存储每一个实例返回的结果,**而且和数组中的顺序是一样的,和哪个先执行完没有关系**
console.log(result)
}).catch(reason => {
// 只要有一个失败,就执行这个方法,失败后不再执行后面的操作
console.log(reason)
})